![]()
Generally, the supplier of goods or services is liable to pay GST. However, in specified cases like imports and other notified supplies, the liability may be cast on the recipient under the reverse charge mechanism. Reverse Charge means the liability to pay tax is on the recipient of supply of goods or services instead of the supplier of such goods or services in respect of notified categories of supply.
There are two type of reverse charge scenarios provided in law. First is dependent on the nature of supply and/or nature of supplier. This scenario is covered by section 9 (3) of the CGST/SGST (UTGST) Act and section 5 (3) of the IGST Act. Second scenario is covered by section 9 (4) of the CGST/SGST (UTGST) Act and section 5 (4) of the IGST Act where taxable supplies by any unregistered person to a registered person is covered.
As per the provisions of section 9(3) of CGST / SGST (UTGST) Act, 2017 / section 5(3)of IGST Act, 2017, the Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification, specify categories of supply of goods or services or both, the tax on which shall be paid on reverse charge basis by the recipient of such goods or services or both and all the provisions of this Act shall apply to such recipient as if he is the person liable for paying the tax in relation to the supply of such goods or services or both.
Similarly, section 9(4) of CGST / SGST (UTGST) Act, 2017 / section 5(4) of IGST Act, 2017 provides that the tax in respect of the supply of taxable goods or services or both by a supplier, who is not registered, to a registered person shall be paid by such person on reverse charge basis as the recipient and all the provisions of this Act shall apply to such recipient as if he is the person liable for paying the tax in relation to the supply of such goods or services or both. Accordingly, wherever a registered person procures supplies from an unregistered supplier, he need to pay GST on reverse charge basis. However, supplies where the aggregate value of such supplies of goods or service or both received by a registered person from any or all the unregistered suppliers is less than five thousand rupees in a day are exempted. ( Notification 8/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dated 28.06.2017). However, vide notification no.38/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dated 13.10.2017, (corresponding IGST notification no.32/2017-Integrated Tax (Rate) dated 13.10.2017) all categories of registered persons are exempted from the provisions of reverse charge under 9(4) of CGST / SGST (UTGST) Act, 2017 / section 5(4) of IGST Act, 2017, till 31.03.2018. This exemption is available only till 31.03.2018.
The provisions of section 9(4) of the CGST Act, 2017, will not be applicable to supplies made to a TDS deductor in terms of notification no.9/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dated 28.06.2017. Thus, Government entities who are TDS Deductors under Section 51 of CGST Act, 2015, need not pay GST under reverse charge in case of procurements from unregistered suppliers.
Registration: A person who is required to pay tax under reverse charge has to compulsorily register under GST and the threshold limit of Rs. 20 lakhs (Rs. 10 lakhs for special category states except J & K) is not applicable to them.
ITC:A supplier cannot take ITC of GST paid on goods or services used to make supplies on which recipient is liable to pay tax.
Time of Supply: The Time of supply is the point when the supply is liable to GST. One of the factor relevant for determining time of supply is the person who is liable to pay tax. In reverse charge, recipient is liable to pay GST. Thus time of supply for supplies under reverse charge is different from the supplies which are under forward charge.
In case of supply of goods, time of supply is earliest of –
• Date of receipt of goods; or
• Date of payment as per books of account or date of debit in bank account, whichever is earlier; or
• The date immediately following thirty days from the date of issue of invoice or similar other document.
In case of supply of services, time of supply is earliest of –
• Date of payment as per books of account or date of debit in bank account, whichever is earlier; or
• The date immediately following sixty days from the date of issue of invoice or similar other document.
Where it is not possible to determine time of supply using above methods, time of supply would be date of entry in the books of account of the recipient.
Compliances in respect of supplies under reverse charge mechanism:
• As per section 31 of the CGST Act, 2017 read with Rule 46 of the CGST Rules, 2017, every tax invoice has to mention whether the tax in respect of supply in the invoice is payable on reverse charge. Similarly, this also needs to be mentioned in receipt voucher as well as refund voucher, if tax is payable on reverse charge.
• Maintenance of accounts by registered persons: Every registered person is required to keep and maintain records of all supplies attracting payment of tax on reverse charge
• Any amount payable under reverse charge shall be paid by debiting the electronic cash ledger. In other words, reverse charge liability cannot be discharged by using input tax credit. However, after discharging reverse charge liability, credit of the same can be taken by the recipient, if he is otherwise eligible.
• Invoice level information in respect of all supplies attracting reverse charge, rate wise, are to be furnished separately in the table 4B of GSTR-1.
• Advance paid for reverse charge supplies is also leviable to GST. The person making advance payment has to pay tax on reverse charge basis.
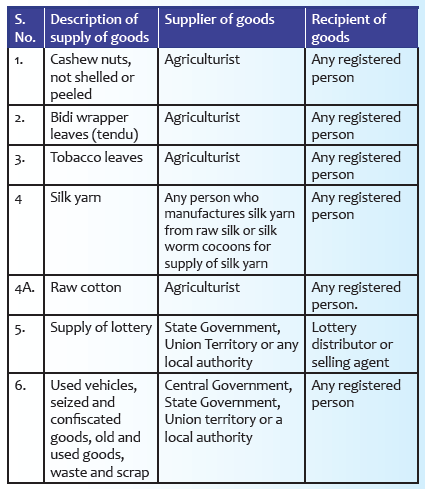
Supplies of goods under reverse charge mechanism:
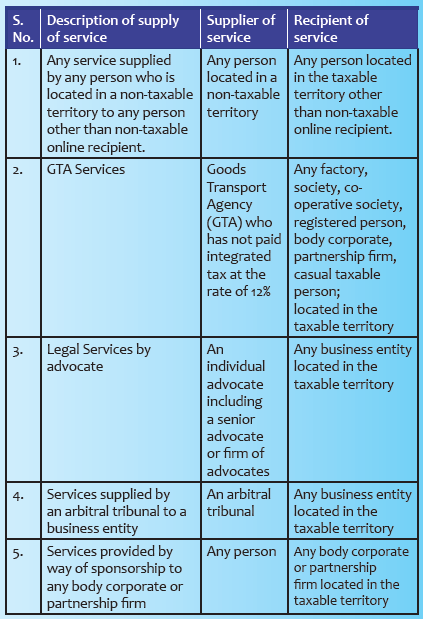
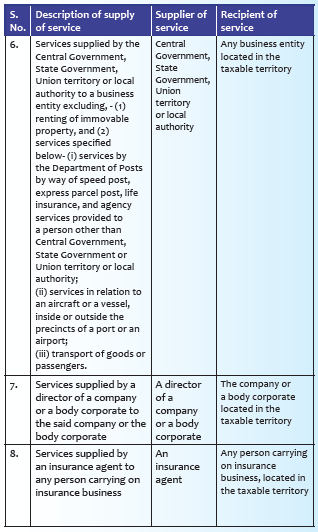
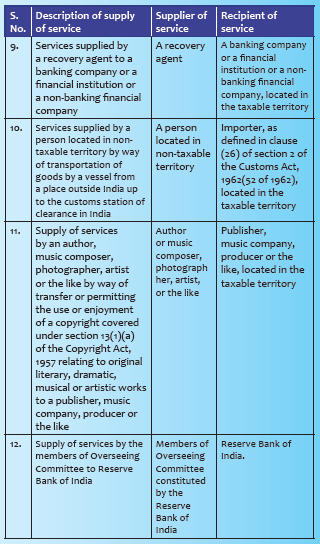
Supplies of services under reverse charge mechanism:
[button color=”” size=”” type=”round” target=”” link=”https://thetaxtalk.com/”]home[/button] [button color=”” size=”” type=”round” target=”” link=”https://thetaxtalk.com/submit-article-publish-your-articles-here/”]Submit Article [/button] [button color=”” size=”” type=”round” target=”” link=”https://thetaxtalk.com/discussion-on-tax-problem/”]Discussion[/button]

