![]()
What is E-Way Bill
-
e-way bill gst is an electronically generated document which is required to be generated for the movement of goods of more Rs. 50,000/- from one place to another.
-
This document is required to be generated online for transportation of goods irrespective of whether such transportation is inter-state or intra-state.
-
Under the GST Regime, generation of the e-way bill is compulsory from 1st Feb 2018.
-
When an e-way bill is generated a unique e-way bill number (EBN) is allocated and is available to the supplier, recipient, and the transporter
Who will generate e-way bill?
The e-way bill under the GST Regime is required to be generated by
-
Every registered person who causes movement of Goods of consignment worth more than Rs 50,000
-
In relation to a supply
-
For reasons other than supply or
-
Inward supply from an unregistered person
-
-
Every unregistered person who causes movement of Goods.
-
The unregistered transporter can enroll on the common portal and generate the e-way bill for movement of goods for his clients.
-
Any person can also enroll and generate the e-way bill for movement of goods for his/her own use.
List of People Who Can Generate an E-Way Bill
| Who | When | Part | Form |
| Every Registered person under GST | Before movement of goods | Fill Part A | Form GST EWB-01 |
| Registered person is consignor or consignee (mode of transport may be owned or hired) OR is recipient of goods | Before movement of goods | Fill Part B | Form GST EWB-01 |
| Registered person is consignor or consignee and goods are handed over to transporter of goods | Before movement of goods | Fill Part B | The registered person shall provide the information relating to the transporter in Part B of FORM GST EWB-01 |
| Transporter of goods | Before movement of goods | Transporter should Generate e-way bill on the basis of information shared by the registered person in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 | |
| If Supplier is an unregistered person under GST and recipient is registered | Compliance to be done by Recipient as if he is the Supplier. | 1. If the transportation of goods is fall under in exemption category then the supplier or the transporter may not furnish the details of conveyance in Part B of FORM GST EWB-01.
2. If supply is made by air, ship or railways, then the information in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 has to be filled in by the consignor or the recipient |
What is the validity of an E-Way Bill?
An e-way bill is valid for periods as mentioned below, which is based on the distance traveled by the goods. Validity is calculated from the date and time of generation of e-way bill and each day shall be counted as 24 hours.
| Distance | Validity Period |
| Less than 100 km | 1 day |
| For every 100 km or part thereafter | 1 additional day |
How to generate E-Way Bill In case the movement of goods is caused by the registered person:
-
The registered person shall first furnish the information relating to the transporter in Part B of Form GST EWB 01 on gst.gov.in and then, the e-way bill shall be generated by the transporter on the basis of the information furnished by the registered person in Part A of Form GST EQB 01.
-
The registered person or the recipient may generate the e-way bill in Form GST EWB 01 electronically on the common portal after furnishing information in Part B of Form GST EWB 01.
-
In case the movement of goods is cause by the registere person and hande over to the transporter for transportation by road, but the e-way bill has not been generate – it would be the responsibility of the transporter to generate the e-way bill.
Note: The registered person as a consignor (i.e. seller) or the recipient of supply as a consignee (i.e. buyer), whether in his own conveyance or a hired one or by railways or by air or by vessel, he is required to generate E-Way Bill.
How to generate E-Way Bill In case the movement of goods is caused by the unregistered person:
In case the movement of goods is done by a person who is not registered under GST, either in his own conveyance or through a hired conveyance or through a transporter, the e-way bill in such a case shall be generated by the unregistered person himself or by the Transporter.
In other words, even if a person who is transporting the goods is unregistered, he would be required to get the e-way bill generated either himself or through the transporter who is transporting the goods.
E-way Bill in case of Sale by Unregistered Person to Registered Person:
If the goods are supplied by an unregistered person to a registered person and the registered person is known at the time of commencement of movement of goods, it would be deemed that the movement of goods is caused by the registered person.
In such a case, the registered person or the transporter shall complete the formalities of the e-way bill.
Format of FORM GST EMB-01:
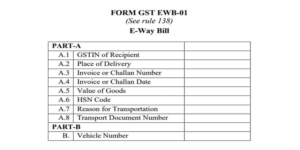
Following points should be kept in mind while furnishing details in GST EWB 01
-
HSN Code in Column A.6 shall be indicated at minimum 2 digit level for taxpayers having annual turnover upto Rs. 5 Crores in the preceding financial yearand at 4 digit level for taxpayers having annual turnover above Rs.5 Crores in the preceding financial year.
-
Transport Document number indicates Goods Receipt Number or Railway Receipt No. or Airway Bill No. or Bill of Lading number.
-
Place of Delivery shall be the PIN Code of the place of delivery.
-
Reason for Transportation shall be one of the following: (1) Supply, or (2) Export or Import, or (3) Job Work, or (4) SKD or CKD, or (5) Recipient not known, or (6) Live Sales, or (7) Sales Return, or (8) Exhibition or fairs (9) For own use, or (0) Others
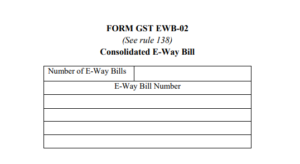
Consolidated E-Way Bill (Multiple Assignment):
If a transporter is transporting multiple consignments in a single conveyance, they can use the form GST EWB-02 to produce a consolidated e-way bill, by providing the e-way bill numbers of each consignment. If both the consignor and the consignee have not created an e-way bill, then the transporter can do so by filling out PART A of FORM GST EWB-01 on the basis of the invoice/bill of supply/delivery challan given to them
What are the Responsibilities of the Transporter?
-
In case the consignor (seller) or the consignee (buyer) has not generated. The e-way bill and the value of the consignment is more than Rs. 50,000, the transporter shall generate Form GST EWB 01. On the basis of invoice or bill of supply or delivery challan.
-
Any transporter transferring goods from one conveyance to another. In the course of transit shall before such transfer and further movement of goods. Update the details of the conveyance in the e-way bill
-
In case where multiple consignments are intended to be transported in one conveyance, the transporter shall indicate the serial number of each individually generated e-way bill in respect of each such consignment electronically on the common platform and a consolidated e-way bill in Form GST EWB 02 maybe generated by him on the GST Website prior to the movement of goods.
Procedure after Generation of E-Way Bill:
- Upon generation of the e-way bill, a unique e-way bill number (EBN) shall be made available to the supplier. The recipient and the transporter on the GST Website. Who may utilize the same for furnishing the details in Form GSTR 1.
- The recipient shall communicate his acceptance or rejection of the consignment covered by the e-way bill within 72 hours.
- In case the recipient does not communicate his acceptance or rejection within 72 hours of the details being made available on the GST Website, it shall be deemed that he has accepted the said details.
Situations where E-Way Bill is not necessary to be generated:
It is not mandatory to generate e-way bill in the following circumstances:-
- The goods are transported by a non-motorized conveyance, such as cycle, rickshaw etc. In general, non-motorized conveyance does not consume energy or cause pollution and provide social equity.
- The goods are being transported from the port, airport. Air cargo complex and land customs station to an inland container depot or a container freight station. For clearance by Customs.
- The goods are transported for a distance. Less than 10 km within the same state from the. Place of business of the transporter to the place of business of the consignee.
- The goods are transported for a distance less than 10 km within the state from the place of business of the consignor to the place of business of the transporter for further transportation.
- In respect of specified goods which are mentioned in this list.
- In respect of movement of goods within such areas as are notified by the concerned state.
Following are the modes of e-way bill generation:
The e-way bill can be generated by the registered person in any of the following methods:
-
Web based system
-
SMS based facility
-
Android App
-
Site-to-Site integration
-
GSP ( Goods and Services Tax Suvidha Provider)
Situation where CANCELLATION OF E-WAY BILL is possible:
In following situation, the e-way bill may be cancelled:
-
Where goods are not transported or
-
Where goods are not transported as per the details furnished in the e-way bill.
-
An e-way bill cannot be cancelled if it has been verified in transitin accordance with the provisions of rule 138B.
-
The facility of generation and cancellation of e-way bill may also be made available through SMS.
What is E-Way Bill
by: CA MONIKA N. RATHI


